Lab: Understanding Docker Images and Layers
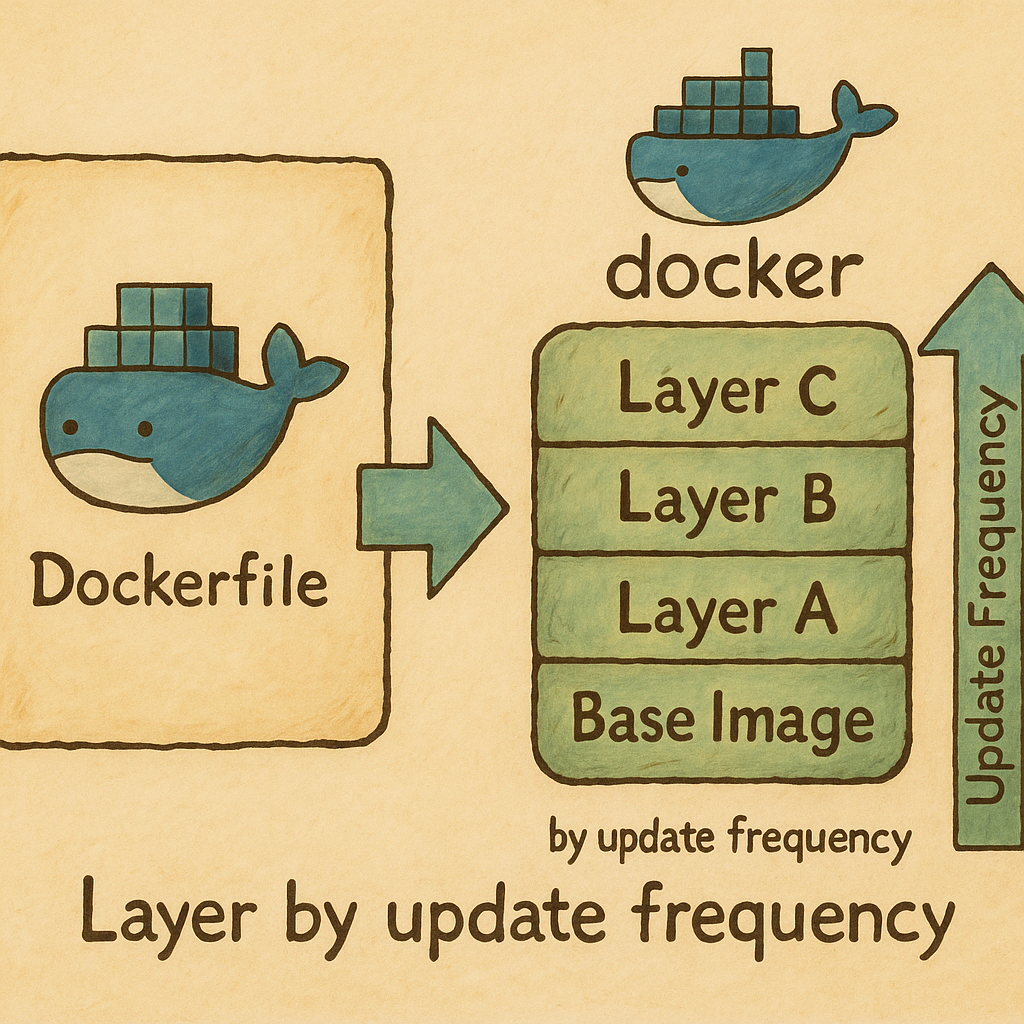
Image Credit: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/understanding-docker-layers-efficient-image-building-majid-sheikh/
Objectives
- Understand what Docker images and layers are
- Learn how to create and inspect Docker images using
Dockerfile - Explore the concept of layers using Docker commands
Key Concepts
What is a Docker Image?
- A Docker image is a blueprint/template used to create Docker containers
- It is static and stored as layers
- Think of it like a recipe: the instructions (layers) define how the image works
What is a Docker Layer?
- A layer is a set of instructions in the
Dockerfile - Each command in a
Dockerfileadds a layer to the image - Layers make Docker images efficient by reusing unchanged layers
Image Credit: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/understanding-docker-layers-efficient-image-building-majid-sheikh/
Hands on Lab
Create a Docker image for running curl
-
Create a new folder for the project:
cd /workspaces/www-project-eks-goat/ mkdir docker-lab && cd /workspaces/www-project-eks-goat/docker-lab -
Create a
Dockerfile:cat << EOF > Dockerfile # Start with a minimal Alpine Linux image FROM alpine:latest # Install curl RUN apk update && apk add curl # Set default command CMD ["curl", "--help"] EOF -
Build the Docker image with a tag:
docker build -t mycurl . -
Verify the image is created:
docker images
Inspect Layers in the Docker Image
-
Check the layers of your image:
docker history mycurl -
Notice how each instruction in the
Dockerfilecorresponds to a layer -
Run the container using the image:
docker run mycurl
Modify and Rebuild the Dockerfile
-
Change the default command to print the version of
curl -
Open the
Dockerfile:cat << EOF > Dockerfile # Start with a minimal Alpine Linux image FROM alpine:latest # Install curl RUN apk update && apk add curl # Set default command CMD ["curl", "--version"] EOF -
Rebuild the image:
docker build -t mycurl .
Reuse Layers for Efficiency
-
Check the image build logs:
docker build -t mycurl . -
Observe which steps were reused.
-
Run the curl command via docker.
docker run mycurl
Explore Image Layers with Dive Tool (Optional)
-
Install
Dive:wget https://github.com/wagoodman/dive/releases/download/v0.12.0/dive_0.12.0_linux_amd64.deb sudo apt install ./dive_0.12.0_linux_amd64.deb -
Analyze the image:
dive mycurl -
Explore the layers and their sizes.
-
Use
inspectto retrieve metadata and configuration details about the mycurl image.docker inspect mycurl
Push the Image to Docker Hub (Optional)
- Log in to docker Hub.
You will be prompted to enter your Docker Hub username and password.
docker login
-
Tag the image:
docker tag mycurl <your-dockerhub-username>/mycurl:1.0 -
Push the image:
docker push <your-dockerhub-username>/mycurl:1.0
Summary
- Docker images consist of layers, with each layer representing a command in the
Dockerfile - Layers enable efficiency by caching unchanged parts of the image
- Tools like
Divehelp visualize layers for better understanding
Tasks
- Modify the
Dockerfileto install and run a different tool (e.g.,htop) - Inspect and explore the layers of your new image using
docker historyanddive
